Docker network
Name space in linux¶
UTS (Hostname+DomainName), User, Mount, IPC, Pid, Net
In docker virtual network interface was used. Bridged network used to connect the containers
A good reference Understanding Docker Networking Drivers and their use cases
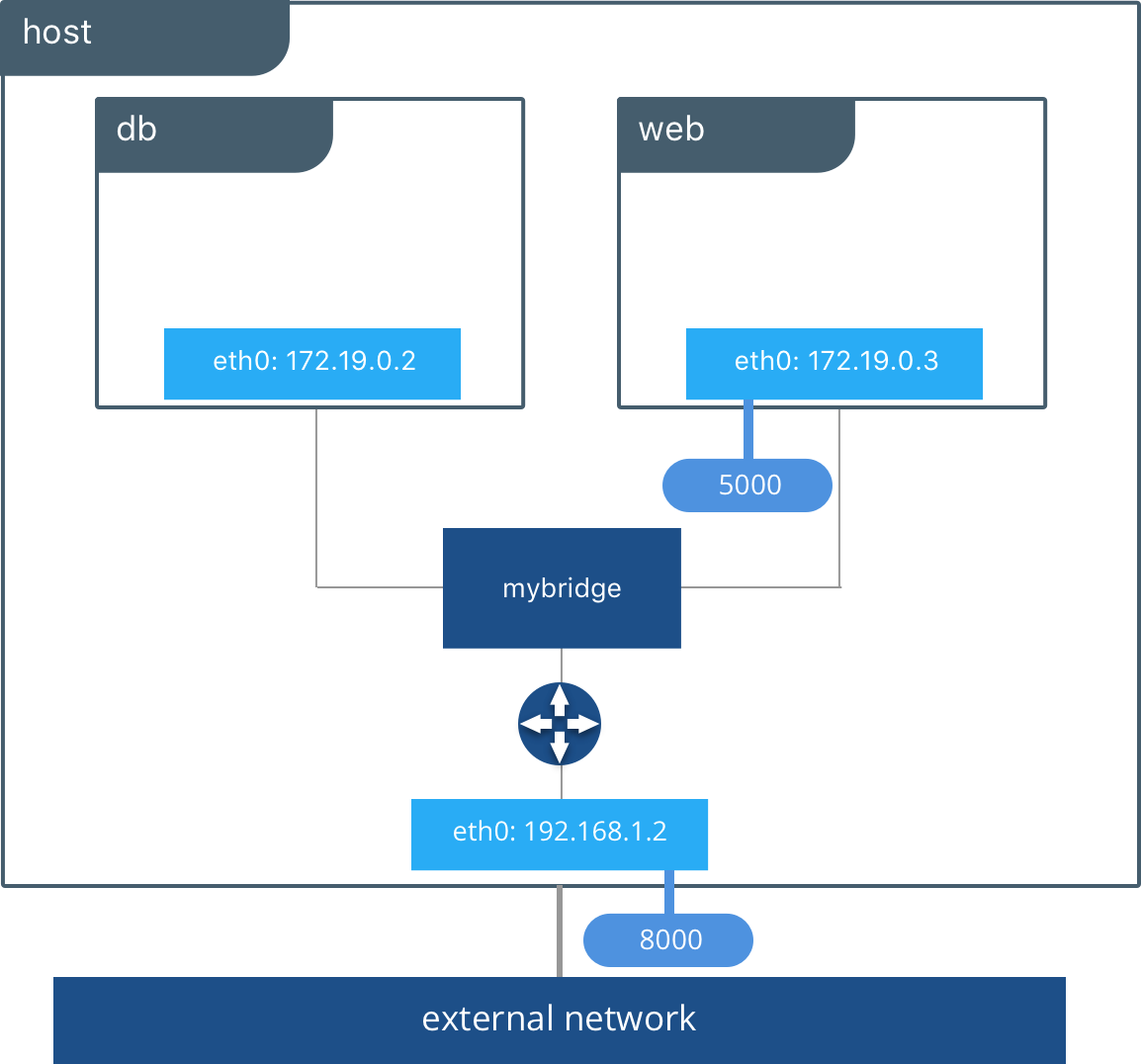
Docker network bridge
Connect to docker network
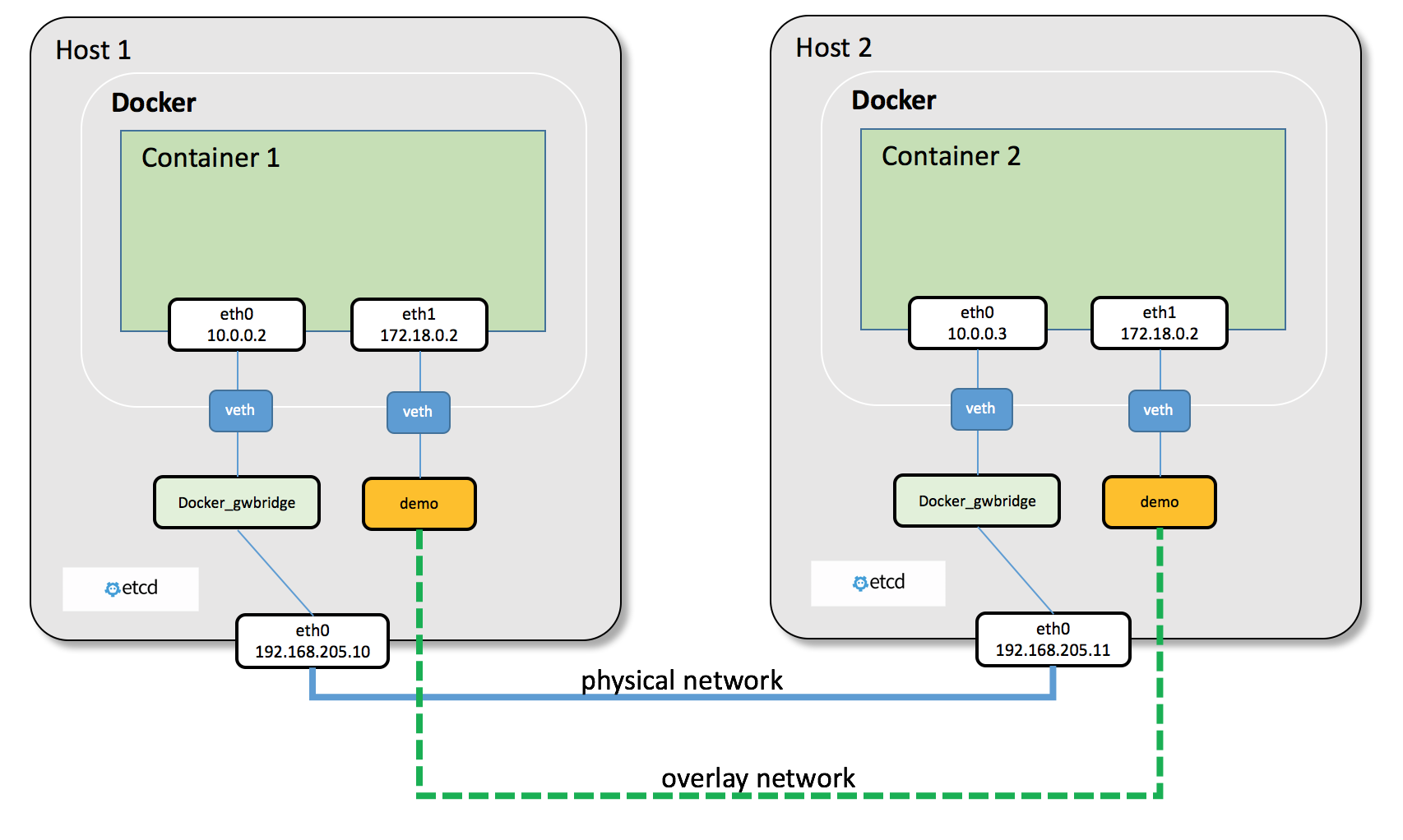
The connection between containers that inside different hosts could be through overlay network.
An diagram from docker-k8s-lab shows how overlay works
Docker networks:¶
- Bridge
- alloc by default when contain starts,
- network: docker0IP 172.17.0.1/16 IP address of your docker
- use
brctl showto check your connection(two busybox container run at the moment): docker0 connected to two interface base1, and base2. base1 can access base2 e.gwget -q -O - 172.17.0.3(-means output to stdout) - host
- access network from host. Share UTS/NET/IPC
- none
- NULL, only have loopback interface
A slightly complicated docker run command¶
docker run --name mydocker1 -it --network bridge -h mydocker1.rayx.me --dns 8.8.8.8 --dns-search rayx.me --add-host www.rayx.me:54.12.17.68 --rm busybox:latest
Above command will create a docker named mydocker1 with bridge network.
The host name mydocker1.rayx.me, use dns 8.8.8.8
in /etc/hosts will have :
Inbound communications¶
docker [container] run -p or docker [container] run -P
* -P will expose all ports, -p will expose specific ports
-
-p
export container port to a host dynamic port (e.g 3001) e.g. start the container docker run --name busybox-web1 --rm -p 80 ray-x/httpd-busybox:v0.2check dynamic port
sudo iptables -t nat -vnLgot:
Chain DOCKER (2 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN all -- docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 DNAT tcp -- !docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:32768 to:172.17.0.5:80
curl 127.0.0.1:32768
Or with docker port
* -p e.g. `docker run --name busybox-web1 --rm -p 8080::80 ray-x/httpd-busybox:v0.2`
-
-p
:: map containerPort to host dynamic port (e.g 192.168.0.2:8080) e.g.
docker run --name busybox-web1 --rm -p 192.168.10.10::80 ray-x/httpd-busybox:v0.2All access to docker 80 will need to through 192.168.10.10 network + a dynamic port -
-p
:: : map containerPort to host and port
e.g. docker run --name busybox-web1 --rm -p 192.168.10.10:8080::80 ray-x/httpd-busybox:v0.2
join other container’s network (share UTS, IPC, Net )¶
start up container b1
docker run --name b1 --rm -it busybox
start up container b2 and join network of b1
docker run --name b2 --rm -it --network container:b1 busybox
run ifconfig on both docker container and the ip address will be the same (in my test both are 172.17.0.2)
b1 and b2 share network and 127.0.0.1 in b1 is same as 127.0.0.1 in b2. e.g start a webserver in b1 and you can use 127.0.0.1:80 to access the http from b2
host network¶
docker run --name b2 --rm -it --network host busybox
/ #ifconfig
docker0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 02:42:32:D3:57:27
inet addr:172.17.0.1 Bcast:172.17.255.255 Mask:255.255.0.0
......
enp1s0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:25:22:26:4E:F8
inet addr:192.168.199.88 Bcast:192.168.199.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::225:22ff:fe26:4ef8/64
.....
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
.....
veth62789e1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 22:3A:F7:11:B3:92
inet6 addr: fe80::203a:f7ff:fe11:b392/64 Scope:Link
.....
--network host container can access the host network
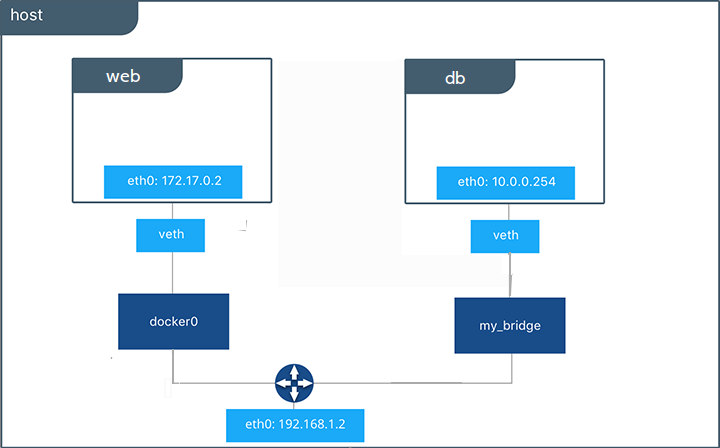
Multiple bridges in a host¶
We could use docker network create to create a new bridge(or host, lo, maclan, overlay etc)
e.g.
docker network create -d bridge --subnet "172.26.0.0/16" --gateway "172.26.0.2" bridge1
Then we can attach container to the bridge1
docker run --name b2 --rm -it --net bridge1 busybox